Expert Care by Dr. Prabhu Karunakaran, Pediatric Urologist in Hyderabad
Circumcision in children
Circumcision is the surgical removal of the prepuce (foreskin), the fold of skin that covers the glans (tip) of the penis. This procedure is carried out for cultural, religious, or medical reasons.
During normal penile development, the glans and the prepuce are naturally adhered to each other. These adhesions are present in most newborns, with approximately three-fourths of boys under the age of five showing such attachments. As children grow, these adhesions typically resolve on their own.
Between the glans and prepuce, small white nodules known as smegma can often be seen or felt. Smegma is a normal physiological substance formed from the accumulation of fatty secretions under the foreskin. Over time, smegma usually resolves spontaneously. Parents should avoid forcefully separating the prepuce from the glans to clean this area, as such actions can cause surface injury to the glans, leading to secondary adhesions.
Circumcision is one of the most debated surgical procedures, with a history dating back centuries. Beyond its cultural and religious significance, it is believed to offer medical benefits, including reduced risks of penile and cervical cancers, sexually transmitted infections (including HIV), and urinary tract infections (UTIs).
Indications for Circumcision
Apart from cultural or religious motivations, circumcision may be performed for medical reasons, including:
- Balanitis (inflammation of the glans)
- Balanoposthitis (inflammation of the glans and foreskin)
- Phimosis (inability to retract the foreskin)
- Paraphimosis (retracted foreskin that cannot return to its normal position)
- Excessively long foreskin
- Recurrent UTIs
- Preventive measures in regions with a high prevalence of HIV or penile cancer regions, ( mostly suited for African continents as of now.
- Penile trauma( injury to the penis or foreskin)
Absolute medical indications include:
- Balanitis Xerotica Obliterans (BXO): A chronic inflammatory condition that leads to scarring of the foreskin, glans, or the external urethral opening.
- Pathological phimosis caused by recurrent episodes of balanitis or balanoposthitis.
BXO affects approximately 1.5% of children. Its exact cause remains unknown.
Timing of Elective Circumcision
The timing of circumcision is a subject of ongoing debate. However, it should be performed promptly when a clear medical indication exists.
For religious or cultural reasons, circumcision should ideally be avoided between the ages of 1.5 to 5 years, a critical phase in a child’s psychological development. If the procedure must be performed during this period, it should be done under sedation or general anaesthesia.
Children older than six, who can understand and cooperate, may undergo circumcision under local anaesthesia, provided they are adequately prepared psychologically. For younger children, general anaesthesia is recommended to minimize distress and ensure a safe, comfortable experience for both the child and the surgeon.
Techniques and Complications
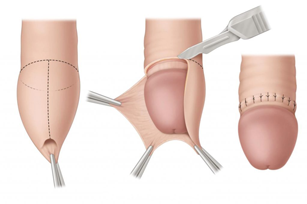
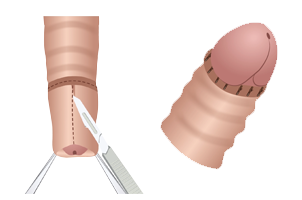
Various techniques are available for circumcision:
- Surgical excision: The foreskin is surgically removed, and the wound edges are closed using absorbable sutures that do not require removal.
- Device-based methods: These involve compressing the foreskin with a bell-shaped plastic device or a stapler device, which causes it to fall off naturally over time.
Complications occur in 1–7% of cases, usually minor. Common issues include:
- Bleeding
- Wound infection
- Inadequate or excessive removal of skin
- Meatal stenosis (narrowing of the urethral opening)
Rare but serious complications may include:
- Severe bleeding
- Glans amputation
- Urethral injury
Risk factors for complications include:
- Lack of sterile conditions
- Procedures performed by untrained personnel
- Poor bleeding control
- Inattention to the anatomy of the glans and urethra
- Mass circumcisions without individualized care
When circumcision is performed in a medical facility under proper surgical conditions, with a Pediatric urologist, complications are exceedingly rare.
Book an Appointment
If you are considering circumcision for your child or need expert advice, schedule a consultation today.


